
A Pakistani cricketer doing the sajda (prostration) on the cricket field after achieving or crossing a milestone, has become an iconic image in international cricket.
The deed is inspired by the procedural act of prostration during the Muslim ritual prayers (namaz) in which a person has to prostrate several times to exhibit his or her submission to the power of the Almighty.
Over the years, this act (among the Muslims of South Asia) has also taken the shape of being a physical expression of giving thanks to the Almighty, in which the person does not necessarily have to be in a mosque or on a prayer mat, performing the ritual prayers.
Instead, to thank God (at a particular moment of personal achievement or even relief) he or she can perform the sajda for a brief moment wherever they deem fit.
Performing the sajda in this context remains to be very much a South Asian Muslim ritual. Though it is mostly seen being performed by sportsmen, it is also quite common for various Pakistani or Indian Muslims from all walks of life to spontaneously (as opposed to ritually) perform it at a joyous moment of one’s achievement or of those close to them.
Roots
No one is quite sure exactly when a part of the act of the sajda migrated from the domain of ritual prayers and evolved into becoming a spontaneous gesture of gratefulness to the Almighty.
But many do believe that this aspect of the Muslim act of prostration is most popular among the Muslims of South Asia, especially those residing in Muslim-majority countries such as Pakistan.
After sprinting across some of the best histories available on Muslim rule in India, I did discover a few isolated episodes in which certain Muslim rulers of the region (between the 12th and 18th centuries) fell into brief acts of the sajda after defeating an enemy (on the battlefield) or after breathing a sigh of relief during a personal or political crisis. But one cannot say for sure whether the practice was also widespread among the common Muslims of the era.
Spontaneity, passion and intuition in one’s spiritual pursuits (over dogma) was encouraged by various Sufi saints and this also went onto shape certain devotional rites that were entirely rooted in the evolving ethos and social dynamics of South Asian societies.
In two of the most detailed studies (by historian Abraham Eraly) of the societies that evolved under the Delhi Sultanate (1206-1536) and Mughal Rule (1526-1707) one can extract an assumption that the spontaneous sajda (performed outside the domain of ritual Muslim prayer and exhibited as a gesture of thanks to the Almighty) might have had its earliest roots in the dominance of Sufism in the region during the mentioned centuries.
It is a well-known fact that the social aspects of the two major Muslim Empires in India were shaped not by the orthodox Muslim ulema and the clergy, but by Sufi saints and their followers.
Spontaneity, passion and intuition in one’s spiritual pursuits (over dogma) was encouraged by various Sufi saints and this also went onto shape certain devotional rites that were entirely rooted in the evolving ethos and social dynamics of South Asian societies. These were thus different from the religious trajectories that Muslim societies took elsewhere.
The sajda in the context that is being discussed in this piece is inherently an informal and spontaneous act, and (like so many other aspects associated with the Muslims of South Asia) this may too be a vestige of a Muslim past shaped by South Asian Sufism.
Muslims belonging to the tradition of ‘folk Islam’ in Pakistan (that is a hybrid form of Sufism), call it Sajda-e-Shukr.
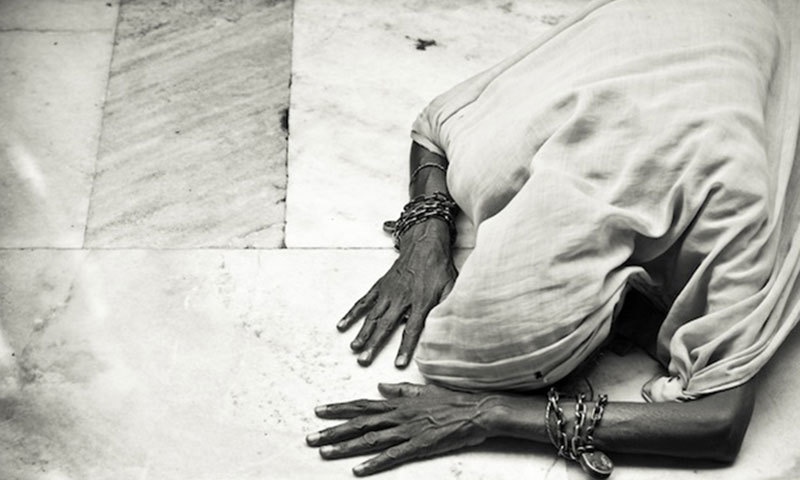

An old woman performing the sajda-e-shukr at a Sufi saint’s shrine.
However, if one looks for it, the more modern roots of the act of performing the informal sajda on the sporting field springs a surprise.
My personal research did not come up with a single prominent episode in which a Pakistani cricketer performed the sajda on the playing field (between 1947 and 1982).
Truth is, even though for more than two decades, the sajda has been largely associated with Pakistani cricketers, yet, it weren’t the cricketers who introduced it on the playing fields.
The pioneers in this respect were the Pakistani hockey players who first performed it in 1978!
But more fascinating is another finding that popped up in my research. The sajda on a sports field is not quite a Pakistani invention, as such.
The first time it was performed in an international arena was at the end of the India-Pakistan final of the 1975 Hockey World Cup in Malaysia.
After the Indians managed to closely defeat the Pakistan side, two Sikh players of the Indian squad fell into sajdas!
This was the first prominent episode. This, in a way, reinforces the thesis that the sporting sajda might have roots in the ancient Sufi disposition of the South Asian societies because the founder of Sikhism, Guru Nanak, was a great admirer of Sufism before he founded the Sikh faith in the 15th century.
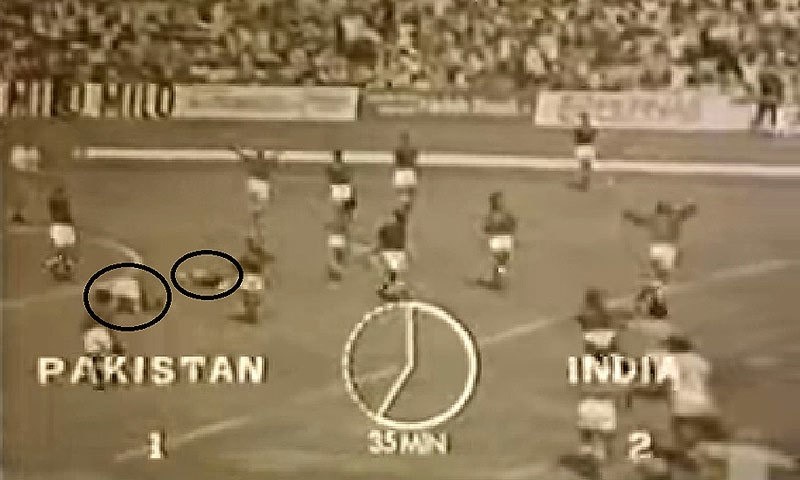

Two Indian hockey team players (both Sikh) perform the sajda during the 1975 Hockey World Cup final against Pakistan.
However, there are some who insist that Pakistani hockey players were performing the sajda in as early as 1973.
Nevertheless, though the Indian hockey players were never again seen performing the sajda, it became a consolidated ritual of Pakistani hockey players from 1978 onwards — especially after Pakistan defeated India in the 1978 Asian Games hockey final (in Thailand); and then downed the Netherlands in the 1978 Hockey World Cup finals in Argentina.
It was also during the final against Netherlands that (non-Pakistani) commentators for the first time commented on the ritual, mistaking it as being an act of the players kissing the ground!
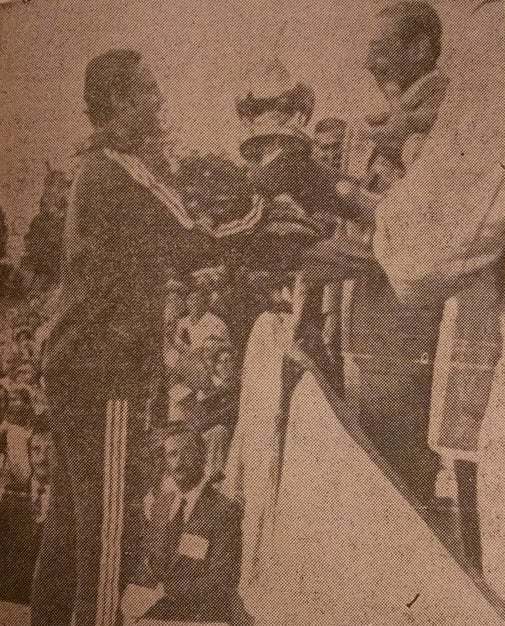

Pakistan Hockey captain, Islahuddin, receiving the 1978 hockey World Cup. He is said to be the first prominent Pakistani hockey player to have performed the sajda (during the 1978 final against the Netherlands).

2014.
By the time the Pakistan hockey team won its third (and second consecutive) Hockey World Cup in 1982, performing the sajda had become an iconic symbol of victory and gratitude associated with the Pakistan hockey sides.
On the other hand, it’s not certain which Pakistan cricketer was the first to perform the sajda on the cricket field.
According to some sources it was the flamboyant opening batsman, Mohsin Hassan Khan, who first performed it after reaching a double hundred at the Lord’s Cricket Ground (against England in 1982).
But the footage of that brilliant innings (now easily available on YouTube) does not show him performing the sajda after reaching his century and then double century — even though he might have.
Another claim suggests that the first sajda by a Pakistani cricketer was performed by master batsman Javed Miandad after he reached a match-saving hundred during the second Test against a strong West Indian side in the Port of Spain (in 1988).
Wily leg-spinner, Abdul Qadir, was also known to have sporadically performed it in the 1980s.
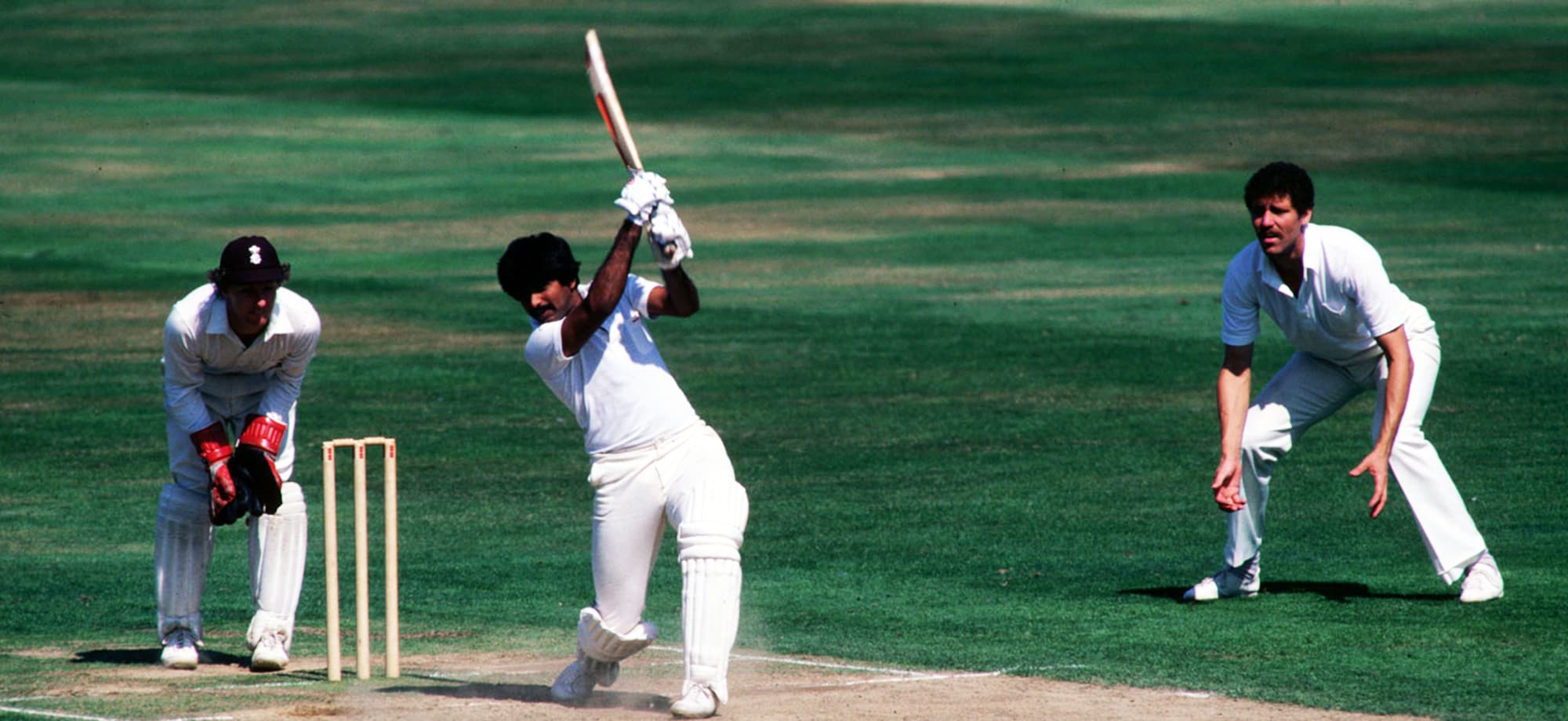

Many believe it was master batsman, Javed Miandad, who (in 1988) was the first Pakistani cricketer to perform the sajda on the field.
But even though the act was clearly inspired by the Pakistan hockey team, the standard and fortunes of the country’s hockey squad had begun to drastically decline from 1986 onwards — after the team failed to defend its world cup title (in England), and crashed out of the tournament.
But this didn’t stop Pakistan’s international squash champion, Jahangir Khan, from occasionally performing the sajda on squash courts, especially after winning tough games (in the 1980s). His successor, Jansher Khan, too would occasionally perform it.
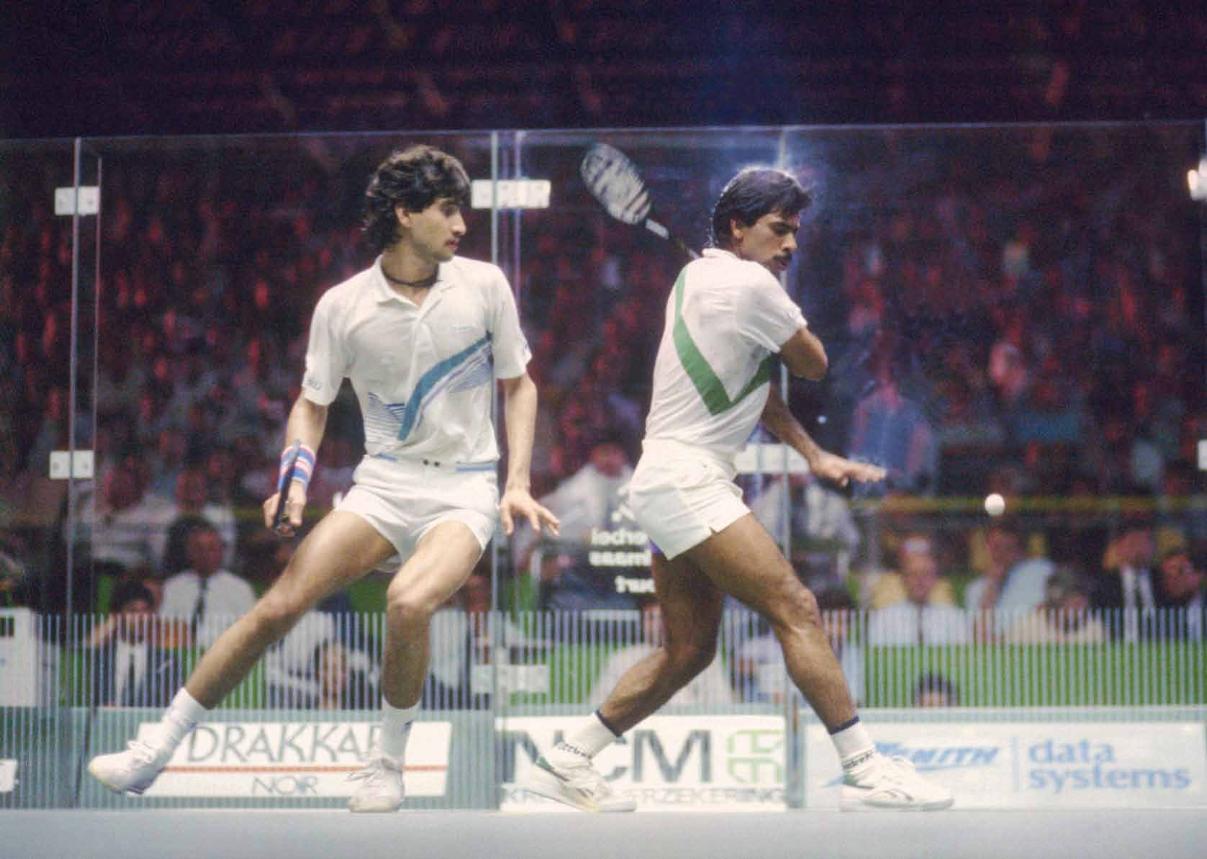

Pakistani squash legends, Jansher Kkah (left) – who was the World No 1 in the 1990s – and Jahangir Khan (right) – the World No 1 across the 1980s – both occasionally performed the sajda after winning tough matches.
Regarding the practice among the cricketers, one can, however, state for sure that the sajda began becoming a mainstay of the country’s cricket culture after millions of TV viewers saw three Pakistani players — Rameez Raja, Aamir Sohail and Moin Khan — do the sajda at the dramatic conclusion of the 1992 Cricket World Cup final in Melbourne in which Pakistan defeated England to bag its first cricket world cup title.
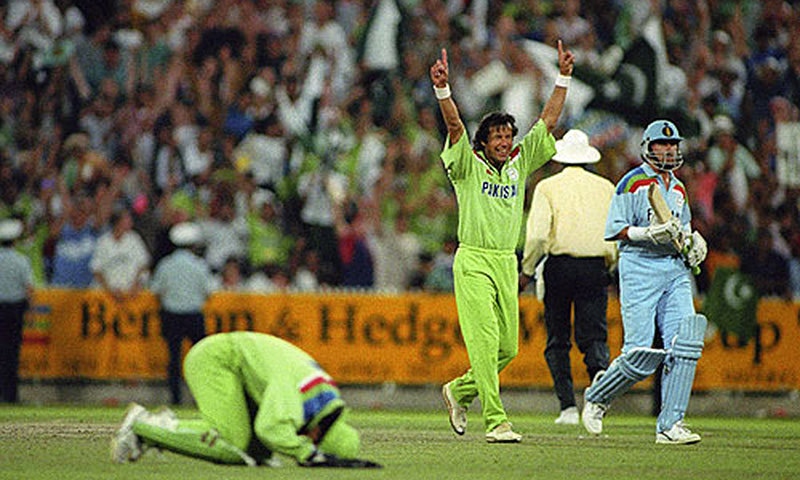

Pakistan win the 1992 Cricket World Cup.
‘Islamization?’
Recently some observers have linked the sporting sajda to the ‘Islamisation’ policies of the state of Pakistan in the 1980s. Policies of that era went on to promote excessive exhibition of religiosity in various sections of the Pakistani society, including sports.
But this is highly unlikely because as we have seen, performing the sajda (during a sporting event) predates the 1980s. It actually emerged during a comparatively more liberal period in Pakistan’s history.
What’s more, in the age of globalization, images of Pakistani cricketers performing the sajda after achieving a sporting feat have also gone on to inspire Muslim sportsmen of other countries as well.
In fact, some Pakistanis belonging to the more puritanical strands of the faith have actually known to have scoffed at the practice, claiming it has nothing to do with ‘true faith’ and is an ‘innovation.’
Whatever the case may be, the sporting sajda has gone on to become an iconic and inspirational part of the country’s sporting culture and is often performed by even the most liberal minded sports personalities. Its supporters also suggest that more than being a show of religiosity, it is an exhibition of humility.
What’s more, in the age of globalization, images of Pakistani cricketers performing the sajda after achieving a sporting feat have also gone on to inspire Muslim sportsmen of other countries as well.
For example, some members of the Algerian football team were seen performing it (after scoring a goal) during 2014’s Football World Cup in Brazil; and so did the famous Muslim member of the Kansas Chiefs, Husain Abdullah, in the United States’ National Football League (NLF).
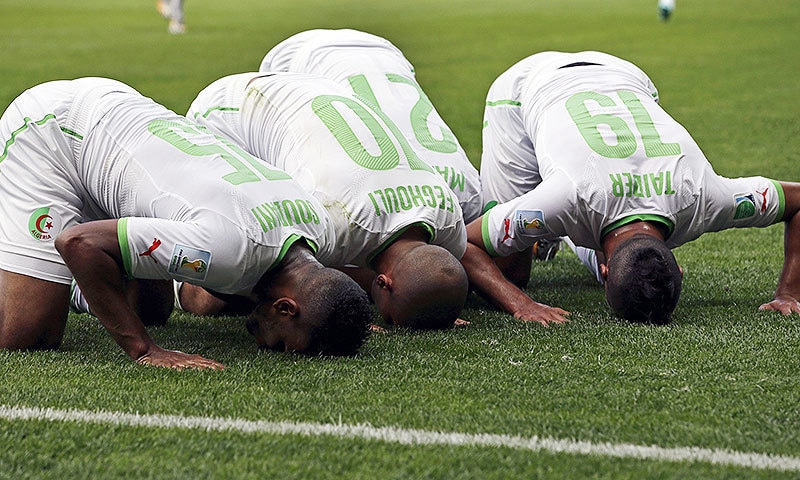

The Algerian football players during the 2014 Football World Cup.
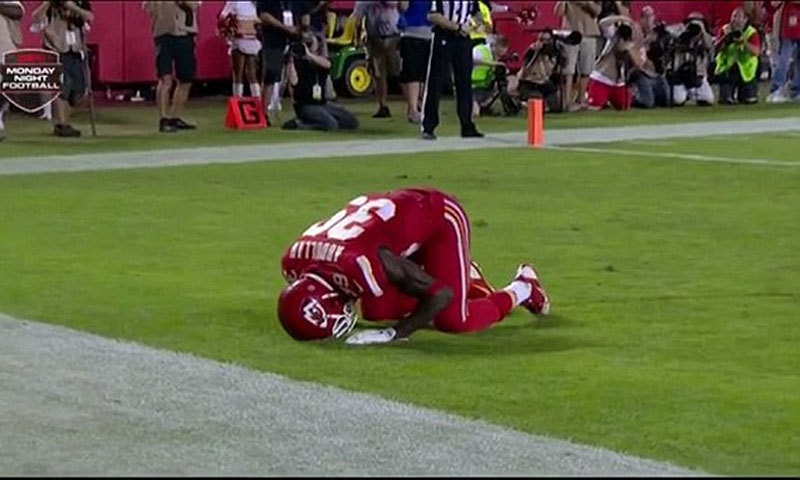

The Kansas Chiefs’ player, Hussain Abdullah, performing the sajda after scoring a touchdown.
